Claiming GST Input Tax Credit (ITC): Key Conditions and Considerations
Published on: Fri Feb 23 2024
Bio (Reveal/Hide)

The Input Tax Credit (ITC) mechanism under India's Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime allows businesses to offset the GST paid on purchases against the GST payable on their sales, effectively reducing their overall tax liability. However, strict conditions govern claiming ITC, ensuring proper tax compliance and revenue protection.
Eligibility
Registered GST taxpayer: Only businesses registered under the GST regime can claim ITC.
Business use: The purchased goods or services must be used for making taxable supplies, further supply, or for the business's benefit. ITC on personal consumption or exempt supplies is not allowed.
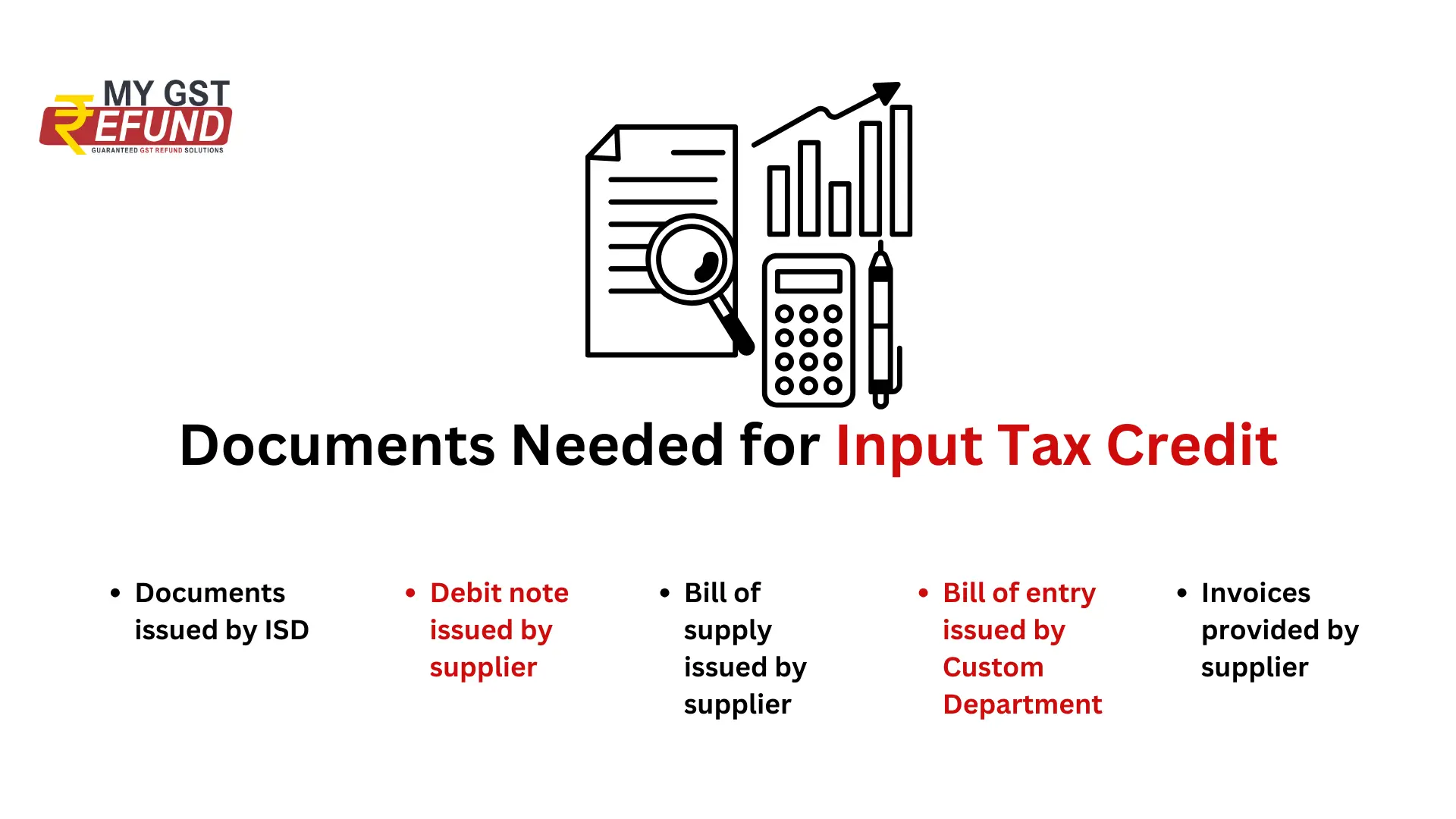
Documentation Required for Input Tax Credit (ITC)
Valid tax invoice: Possess a valid tax invoice, debit note, or other prescribed document issued by a registered supplier. E-invoice requirements must be adhered to where applicable.
Receipt of goods/services: ITC can be claimed only after receiving the goods or services. For supplies received in installments, ITC can be claimed on receipt of the last installment.
Tax compliance
Supplier's tax payment: The supplier must have paid the GST to the government and filed the required returns.
Timely return filing: File your GST returns (GSTR-3B) within the prescribed deadlines.
Payment within 180 days: For purchases above ₹10,000, payment to the supplier must be made within 180 days from the invoice date. Failure to do so may result in reversal of ITC and interest penalty.
Additional considerations
Reverse Charge Mechanism: In certain cases where the recipient is responsible for paying GST (reverse charge), a self-invoice can be used to claim ITC.
ITC Restrictions: Be aware of specific restrictions or limitations on ITC eligibility for certain goods or services (e.g., food and beverages, outdoor catering, construction contracts).
Matching Invoices: Ensure proper matching of tax invoice details (invoice number, date, value, tax rate, etc.) between your records and GSTR-2A/2B. Mismatches could lead to ITC disallowance.
Timely Action: Address mismatches or discrepancies promptly by communicating with suppliers or filing rectification statements to safeguard your ITC claims.
Professional Guidance: For complex transactions, non-resident businesses, or specific guidance, consult a tax advisor or GST expert.
Examples
A restaurant can claim ITC on the GST paid for ingredients, utilities, and other business expenses, but not on food purchased for personal consumption.
A manufacturer can claim ITC on the GST paid for raw materials, machinery, and equipment used in production, but not on furniture for its office.
A travel agency can claim ITC on the GST paid for hotel bookings and transportation for clients, but not on travel for its employees' holiday.
Related Posts






